Consumer mindsets are evolving at an accelerating pace.
While it wasn’t long ago that shoppers could be satisfied receiving the tiniest of details from a product’s journey before it came into their possession, years of unsustainable and unethical practices within retail supply chains have begun to tarnish the relationships between businesses and their customers.
Understandably, customers are increasingly demanding that the traditionally opaque supply chains that serve them are made more visible – and they’re using their wallets to back and promote these values. As a result, power has shifted, and unless retailers want to become obsolete, ignorance and dishonesty must be replaced with clarity and accountability.
Especially since — over the past 18 months — the pandemic has intensified this scrutiny, and it seems that now, for retailers to survive, they must relinquish their use of transparency as a novel marketing strategy and view it as a necessary process to be implemented into everything they do.
Transparency as a marketing tool is nothing new, businesses have been branding their performance as a method of storytelling that highlights their morality and pulls audiences in for a while now. Greenwashing, however, has become a concerning result of this trend, with companies picking and choosing what to report and positioning their activities in a positive light.
In fact, in the Business of Fashion’s and McKinsey & Company’s The State of Fashion 2020 report, almost 20% of executives claim that radical transparency is one of the top three themes impacting their business due to changing consumer desire for genuine and clear information.
What Does a Radically Transparent Supply Chain Look Like?
Radical transparency defines the complete disclosure of information at every link of a retailers supply chain. This includes everything from the sourcing of raw materials, water usage in textiles dying, factory working conditions, the environmental impact of goods distribution, and customer care instructions.
In the past few years, many organisations have led the charge regarding supply chain clarity. For example, in just the apparel sector exists Fashion revolution Eco-Age and Good on you – all of which currently hold fashion retailers accountable over the impact of their supply chains by taking different approaches to the promotion of reporting.
And reporting is the cornerstone of supply chain transparency, providing a window into the practice’s businesses abide by. H&M — leaders in supply chain transparency — are among many retailers who have aligned their manufacturing reporting with Transparency Pledge Reformation takes this a step further, making the environmental impact and traceability of their products public.
Yet, the widespread adoption of end-to-end supply chain clarity is limited and slow. While most businesses have begun to embed transparency into their internal operations and with direct suppliers, processes beyond their control – for the most part – remain opaque.
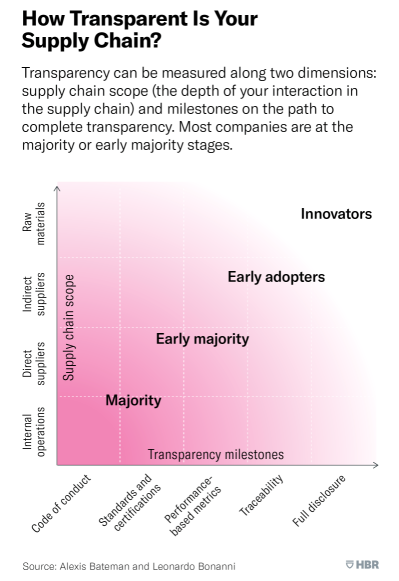
As a result, the companies that can trace their products’ raw materials are categorised as pioneers of supply chain transparency, whilst businesses that can track the activities of their indirect suppliers are ahead of the curve. Yet, for the majority of companies, moving towards full disclosure reporting can seem like an impossibly far milestone to reach. Nonetheless, it is one they must begin striving towards now.
Why Prioritise Transparency Now?
While many retailers readily look to improve their supply chain transparency, for many others, full-disclosure reporting is a practice being pressured upon them by both direct and indirect stakeholders. These different parties desire open and honest information for various reasons. Here we discuss the mindsets of these stakeholders and explore the reasons behind their demands for radical supply chain transparency:
1. Customers
The post-pandemic retail sector is filled with innovation that attracts the re-emerged consumer whose activism has been heightened by COVID-19. Multiple lockdowns had given the world time to re-evaluate its values, especially when last year, there was no good excuse to look away from societal issues that took the world stage, such as climate emergencies, poor factory conditions, and racial injustice. As a result, contemporary consumers are more scrutinising now than ever before and want the businesses they shop with to take accountability when problems within their internal operations are uncovered.
Sustainable and Ethical Practice:
It is arguably customers who drive retail’s interest for heightened clarity through their passion for advocating brands with sustainable products and ethical operations. In fact, 64% of shoppers look for ethical or sustainable features when making a purchase, and according to researchers at MIT Sloan School of Management, they may be willing to pay 2% to 10% more for products from companies that provide greater supply chain transparency.
In being able to see the impact of their purchases more clearly, customers are not only able to build trust with a retailer but become more assured that their own behaviours align with the values they hold.
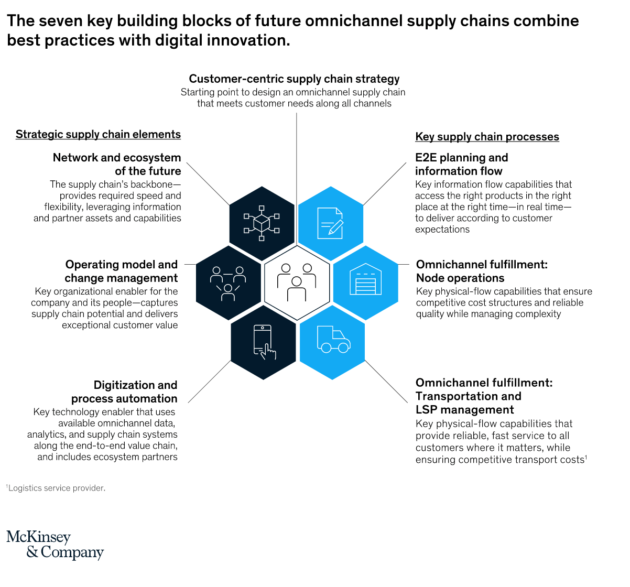
Omnichannel:
Customer-centricity is key to post-pandemic supply chain success as demand for goods becomes increasingly uncertain and erratically patterned. The growth of omnichannel means that shoppers expect retailers to cater to them at the physical and digital touchpoints they more fluidly move between in the wake of the pandemic.
By improving the transparency of their supply chains, retailers could much more readily provide the services created by the omnichannel shopping experience, such as real-time inventory visibility and same-day delivery fuelled by digitisation.
2. Employees
Employees are core stakeholders that the shift towards transparency would most impact. Making their working environments unambiguous and their everyday tasks clear to external audiences allows employees, customers and investors to hold retailers accountable in a public domain.
Welfare: According to Anti-Slavery International, there are 16 million people trapped in forced labour within the supply chains of businesses that supply our goods and services. Supply chain transparency is a small step to providing workers more protection over workplace conditions, wages, and personal agency, helping mitigate the risk of external suppliers taking advantage of labour in the sector.
As a result, by enhancing supply chain transparency, businesses are able to track the social impact of their operations and shine a light on grey areas within their own chains that they may not have complete control over.
3. Investors
Last year, Boohoo lost more than 1.5 billion euros in market value after it was uncovered that workers manufacturing their products earned less than minimum wage in poor working conditions. So making it clear that now more than ever, customers aligning their purchases with their values will have a tangible impact on revenue.
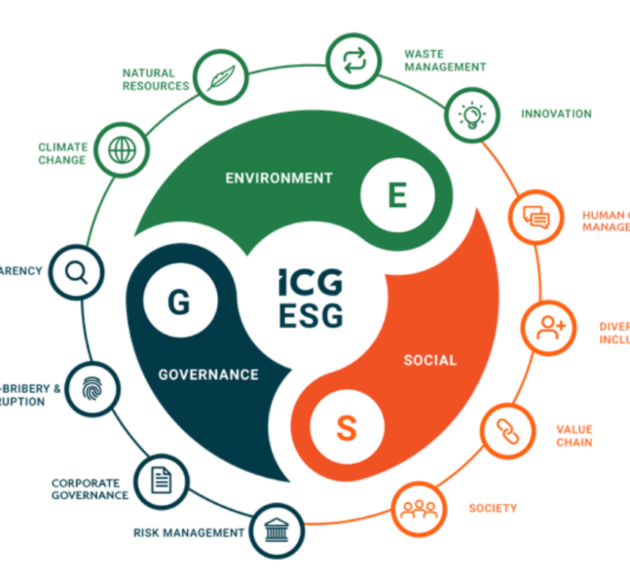
Return on Investment: For investors, the intrinsic link between supply chain controversy and loss in market value is a concerning risk. For example, violations in ESG practices were estimated to have erased almost half a trillion dollars’ worth of value from public companies from 2015 to 2019. ESG stands for environment, social and governance. All three domains increasingly feed into an investors decision to back a company beyond financial projections.
So, with investors progressively looking to work with businesses that have a positive impact, transparency is a firm method of proving compliance with every step of the EGS chain that can easily be mapped to the supply chain.
Transparency and Visibility: One Cannot Exist Without the Other
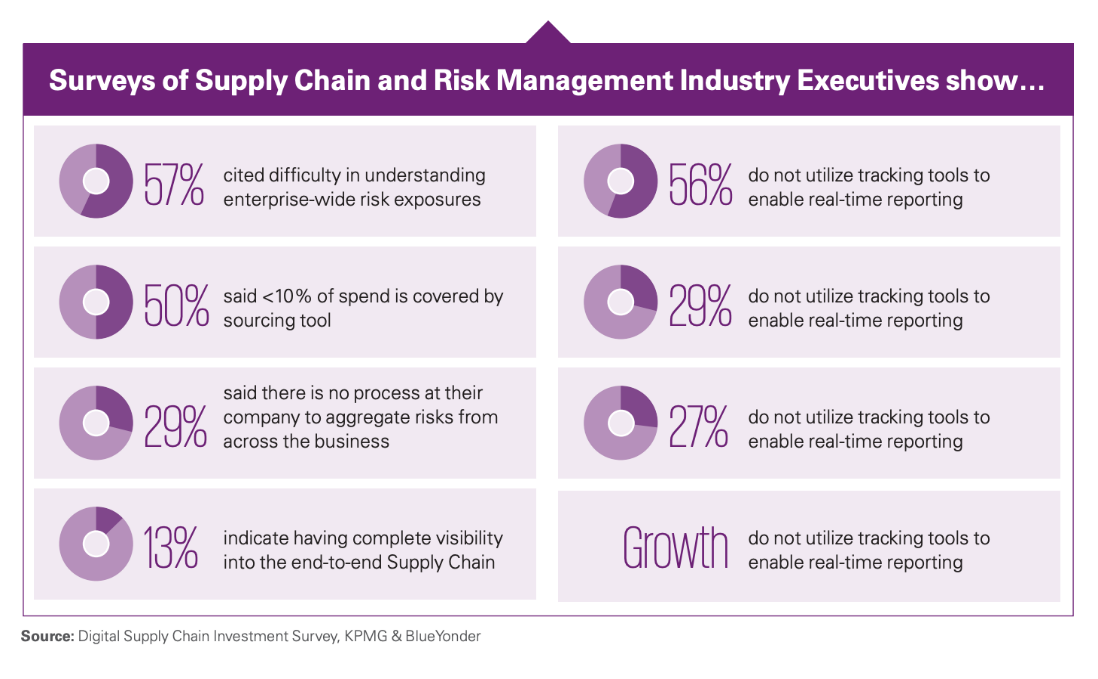
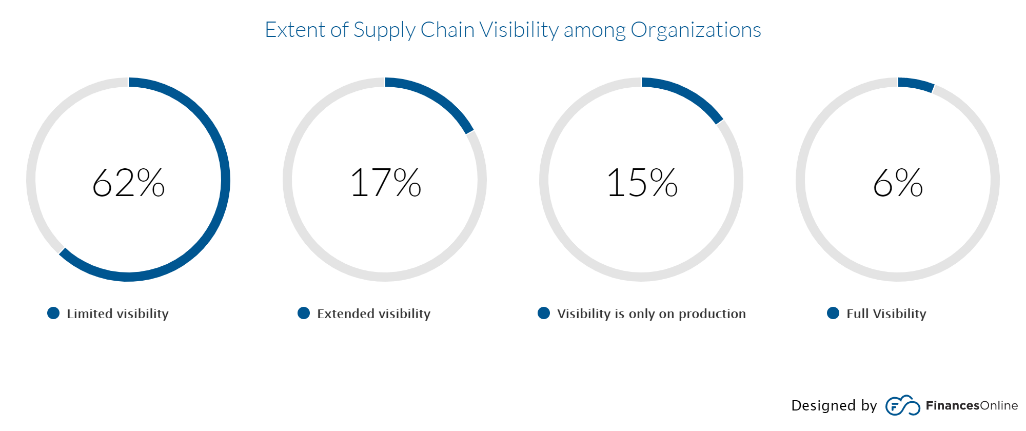
Now that we have made a case for supply chain transparency, there is still the question of how these typically tangled and murky operations can become crystal clear when only 13% of retail executives currently describe having end-to-end visibility.
Although often and mistakenly interchanged for one another, transparency and visibility are two separate concepts when it comes to supply chains, but for retailers, one cannot exist without the other. Therefore, if retailers are to make their supply chains more transparent, they must first be made more visible.
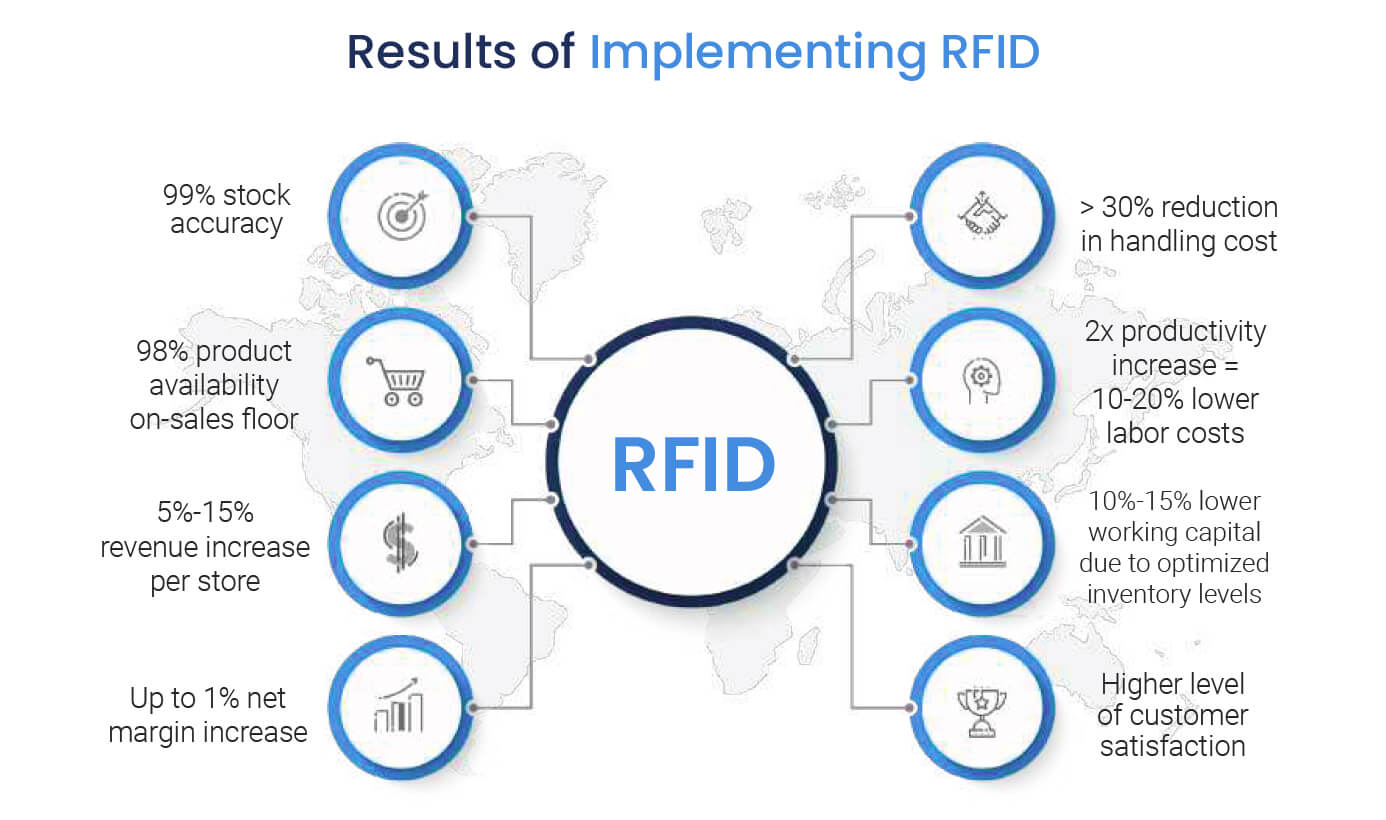
Implementing RFID technology can help provide retailers with unparalleled inventory tracking. By tracing stock at item-level from the factory to warehouse to shop floor, RFID can help retailers improve sustainable and ethical practices within their operations in the following ways:
Post-Purchase Care: By recording raw materials, RFID can assist retailers in tracking the origins of their products and enables them to have a longer life by tracing their composition and helping owners care for their items better.
Carbon Footprint Tracking: RFID technology can follow inventory at item-level at every step of their journey, allowing businesses to calculate the environmental impact of every individual product and correctly offset it.
Workload Easing: RFID also helps retailers ease the strain of workload within factories and distribution centres by taking the place of manual tasks such as stocktake and locating lost items.
Excess Inventory: Limiting the risk of waste products, RFID can help retailers monitor stock and manage future orders with these insights by distributing inventory to locations with high demand or designing a new collection whilst avoiding the features of underperforming products.
Manufacturing Conditions and Compliance: Tracking products back to their production source allows stakeholders to hold retailers accountable if the working conditions and practices of their internal and external factories are below standards.
Implementing Radical Change
Although organisational resistance to change is weakening, according to a recent survey by Accenture, 94% of experts said there is still no obvious effort to align the organisation’s culture with the goals of the change they intended to create. Yet the fact is, supply chains need to become radically more transparent, whether retail wants to embrace it or not.
The pandemic has exemplified change as an uncomfortable yet vital feature of business survival, and technology has been the great enabler for catalysing operational honesty and transparent reporting. But there is still much more to be done. End-to-end transparency is still a rarity, and retailers will need to push forward to experience the benefits of stakeholder satisfaction.
Book a consultation with Detego today to discover how RFID can help your organisation implement lasting and radical change through increased visibility.
Cloud-hosted RFID software
The digital supply chain
Detego’s RFID-based warehouse software enables retailers to automate and dramatically improve their receiving, picking/packing and shipping processes in factories and/or distribution centres. These steps are vital parts of an end-to-end RFID solution, providing full visibility across the entire supply chain.
It is no exaggeration to say that the past year has been destructive yet transformative for the retail sector. The pandemic caused a considerable dip in the performance of stores worldwide, and now in the wake of – what we hope were – the worst days of Covid-19, recovery is the keyword on everyone’s mind. In the three months since physical stores reopened in the UK, brick and mortar retailers have begun implementing the strategies they meticulously designed when all they could do was watch and wait as e-commerce cannibalised their market share.
Many of these retail strategies were built upon the review of supply chain management, with 70% of Europe’s 30 biggest retailers using Covid-19 as a reason to reevaluate how they’re operated. Yet even now, as sales start to return to pre-pandemic levels — with physical retailers reporting the strongest summer sales in four years — it is clear to see that these strategies are still grappling with how to manage uncertainty.
So, as a result of recent customer demand exceeding expectations, stock is at its lowest level in the entire 38 years of the CBI’s records. Caused by limited inventory visibility — a topic we covered in an article last month — it is a problem that is continuously overlooked in retail, even though its impact reverberates throughout entire business models, and its solution remains relatively simple.
RFID is an easy and practical method of monitoring inventory throughout the entire supply chain, helping retailers respond to market fluctuations navigate the chaos of today’s retail environment. So, could this technology be the answer to brick-and-mortar’s strategic recovery?
Why the Time is Right for Retail’s Digital Maturity
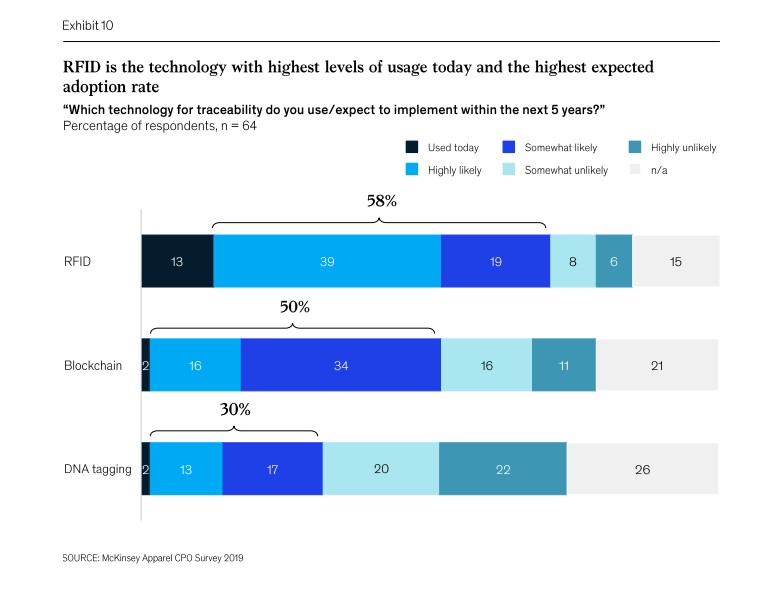
It has been a long time — around 20 years in fact — since RFID was first introduced as a change-making technology to supply chain management. From then on, widespread adoption has been slow yet robust amongst few innovative retailers who understood the need to invest in software providing stock visibility. But now that Covid-19 has accelerated retails digital adoption by at least three years, RFID has experienced a recent uptick in implementation RFID has experienced a recent uptick in implementation, as use cases become as clear as ever before.
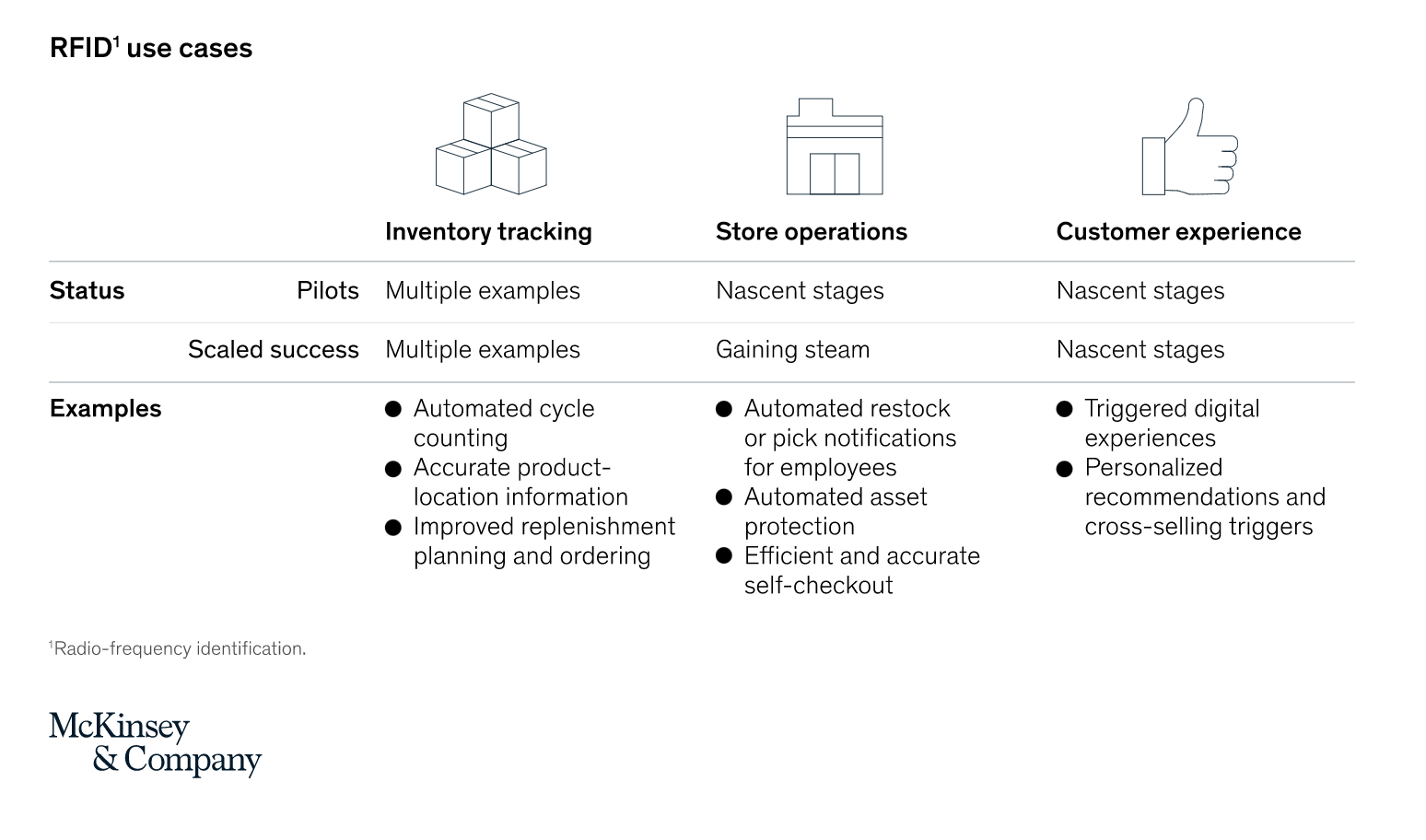
A recent article exploring RFID’s renaissance by McKinsey & Company outlines the current stages these use cases are at with store operations and customer experience only beginning to be explored as solutions. This growing adoption of RFID we see by retailers is comparable to the increased implementation of QR codes, which are currently experiencing a resurgence as COVID-19 heightens demand for digital touchpoints in physical spaces.
The blending of online and offline is one of two fundamental changes to the retail landscape that have ripened RFID for success:
1. Omnichannel Fluidity:
Consumers’ have newfound comfort in moving between digital and physical channels as social restrictions pushed them into online environments over the past year. And as these digitally savvy customers begin to use more omnichannel touchpoints, retailers will need to manage item-level data in real-time to consistently cater to customers as they shift from clicks to bricks.
The second key difference to the retail sector since stores first shut their doors in early 2020 is the ambiguous long, and short-term needs of customers as the context of their everyday lives unpredictably shift on both local and global scales:
2. Uncertain Market Demand
So as the future of the new normal remains blurry, retailers will need to become more responsive to changeable market demands and make sweeping supply chain adjustments to mitigate the risk of wasted inventory in addition to granular decisions to fulfil localised and personalised, item-level needs.
Inventory Visibility Helps Retailers to Anticipate Change and Respond to the Unexpected
The cycle of instantly catering to consumer demands across multiple channels while being powerless to predict them makes RFID all the more compelling as a solution. The technology is being used to increase retailer’s profitability by helping businesses to empower their store processes. RFID efficiently replaces arduous manual stock-takes and regularly updates inventory levels, so stores have a clear real-time view of product location and availability. This not only enhances brick-and-mortar stores as fulfilment centres but allows them to operate accurately across digital and physical channels.
Yet crucially, to mitigate risk, we should not forget that inventory visibility is more than simply viewing stock levels. It also can contextualise inventory information with item-level data – such as size, colour, and price – helping buyers and merchandisers to improve their practices with insights.
The Retailers Already Using Inventory Visibility Software to Strengthen their Post-Pandemic Customer Experiences
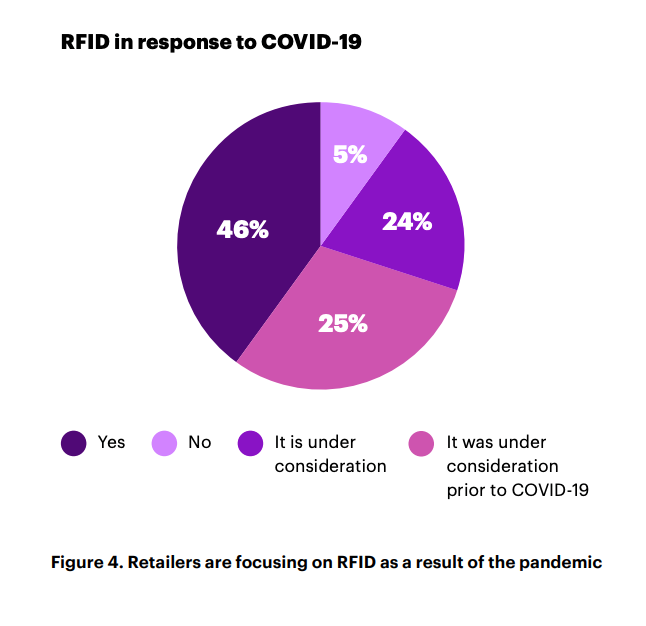
While there are many examples of RFID’s application in industry, recent instances of retailers emboldening their use of the technology to strengthen their post-pandemic strategies are impressive. 46% of respondents to recent Accenture research indicating that they have focused on RFID in response to COVID-19. And although the term inventory software may seem like a dull back-end technology, there are already many new use cases emerging and harnessed by retailers in innovative ways to modernise their offerings.
In-Store Customer Experience
As physical retailers look to win back their market share, the role of stores has needed to evolve with customer demands. For example, research last year by RetailExpo uncovered that 31% of consumers want employees to help with out-of-stocks. And luckily for retailers, store staff are becoming more adept at switching between online and offline more frequently, allowing customer-facing employees to underpin their daily activities with inventory insights such as product availability, reservations and returns.
Mango: Fashion retailer Mango – whose parent company Inditex began to adopt RFID back in 2014 – recently launched a new physical store that combines RFID with deep learning. Generating data, store staff can glean insights using stock performance and availability to enhance their ability to deliver excellent customer service.
Farfetch: Heritage luxury brand Chanel’s collaborative store with Farfetch uses RFID to power consumer-facing services such as changing room mirrors to monitor engagement with inventory and up-sell similar and complementary products. By underpinning the physical shopping experience with data, customers are able to access a level of personalisation often reserved for online commerce.
Omnichannel Continuity
The sudden surge in omnichannel implementation is a topic we discussed in detail in a previous article, and its importance in the current retail environment cannot be underestimated. For the many retailers operating multiple commerce channels throughout the pandemic revisiting their omnichannel capabilities will have been imperative as the purpose of their online and offline environments are no longer siloed.
Reiss: On the unpredictable UK high street, Reiss has managed to stay solid and stable. Achieving a 4% uplift in sales with Detego, the retailer implemented RFID into its stores before the pandemic hit. So now, when purchasing from Reiss’ online store, customers are provided with the option to collect purchases from their brick-and-mortar shops.
Extending Product Life Cycle
We are seeing the emergence of independent resale businesses, and many existing retailers are beginning to consider extending the life of their stock by rolling out buy-back and circularity schemes. Yet, lack of supply chain transparency has for a long time been a growing concern for consumers who demand more ethical and sustainable practices within the sector. So as the industry continues to contemplate the future of products beyond initial consumption, RFID presents itself as a valuable tool for shedding light on an item’s circular journey.
Vestiaire Collective: In collaboration with Alexander McQueen, the luxury resale marketplace Vestiaire Collective uses NFC tags to authenticate its products. This collaboration benefits sellers and buyers by helping owners find value in their wardrobes and reassures consumers of the validity of their products.
eBay: Similarly, the online marketplace eBay uses NFC technology to help users verify the authenticity of purchases of luxury handbags. This is a somewhat important milestone for businesses that want to emphasise their reliability when working with designer goods.
For many retailers, Covid-19 has awakened then to the risks of merely dabbling with technological innovation — rather than fully immersing themselves in it — and brought to light the blind spots within their supply chains that previously flew under the radar. But there is no one size fits all when it comes to technology, and these retailers have expertly harnessed inventory software to their individual requirements, carving out spaces for the technology to fulfil specific objectives within their operations.
Building RFID into Retail Supply Chain’s is as Easy as Ever Before
One of the common myths about RFID is the apparent steep costs of its integration. But in reality, using the technology is becoming increasingly cost-effective as retailers see an ROI of more than 10% whilst the price of RFID components such as readers and tags drop. And as technology matures, RFID is more precise than ever. As a result, most businesses see a boost to accuracy rates in stock, helping store staff make better use of their time carrying out customer fulfilment instead of stock-takes.
Additionally, where complete RFID integration into supply chains was a complex operation with many moving parts, its currently high global adoption within many continents will make coordinating far-reaching stock journeys easier and agile.
RFID and the Future of Brick-and-Mortar Innovation
There are so few technologies that have the opportunity to impact the everyday experiences of so many store stakeholders — from customers and sales assistants to buyers and merchandisers, all the way through to manufacturers — and RFID is one of them.
As the post-pandemic consumer emerges expecting complete omnichannel continuity to attain their trust and loyalty, inventory visibility could be the key to future-proofing any retail business in both online and offline environments. And retailers now know the importance that understanding their operations in detailed real-time plays in managing the flow of goods with more control and agility.
So although we can all agree that the technology is nothing new, RFID should not be ignored as the answer to unique challenges retailers face today and the essential tool for building dynamic in-store solutions for the future
Cloud-hosted RFID software
Stock accuracy, on-floor availability, and omnichannel applications in stores.
Detego Store is a cloud-hosted RFID solution which digitises stock management processes, making them more efficient and more accurate. Implemented within hours, our multi-user app can provide intelligent stock takes and a smart in-store replenishment process. Later, you can scale the solution to offer omnichannel services and effectively manage your entire store operations with real-time, item-level inventory visibility and analytics.
The retail industry is changing fast. Customer preferences are changing, the balance of power between online and offline shopping is shifting, and as a result, operations and business models are becoming more complex than ever before. While these changes have been ongoing for some years, the pandemic has accelerated the shift and left retailers with no margin for error.
In a rapidly changing landscape, many retailers have done well to pivot effectively. However, with the pandemic and digital disruption ramping up most are unprepared in terms of supporting technology to ensure these new strategies are profitable long-term.
Chief among these is the lack of reliable product visibility that many retailers struggle with. For brands introducing new operating models, reopening stores after lockdowns, and selling to customers in more ways than before (like Omnichannel) not having a reliable view of products can severely hamper the profitability and effectiveness of such services.
What is inventory visibility?
Visibility in retail refers to a brand’s ability to see and track its merchandise across stores and supply chains. Simple enough in theory, but actually achieving and maintaining this is far more complicated.
Accurately tracking products is the first hurdle where many retailers stumble. For stores, it comes down to being able to perform regular stocktakes, several times a week rather than several times a year. With ‘standard’ technology like barcode scanners, this is simply impossible, even with a world-class ERP system tracking what’s officially coming in and out. Without physically validating what is in a store, the accuracy levels will quickly drop to around 70% due to factors like operational errors, stock counting inaccuracies and theft.
In the supply chain, on the other hand, it’s not a case of an inaccurate view of stock, but often no real visibility at all. Retail supply chains often only track ‘cartons’ (or boxes) throughout the item journey, since counting the contents of each item again is either impossible or entirely too time-consuming. This means most supply chains run on what should be present in each carton and shipment, but mispacks and theft are all too common.
The other reason many retailers don’t have real visibility over their products is that their IT and inventory management systems only work on an SKU level and not an item-level. For a full breakdown on what this means, read this article.
So, what is this lack of visibility costing retailers?
Everyday, stores lose sales due to poor product visibility
The industry is much more focused on achieving product visibility now due to the Omnichannel surge but there is a more immediate issue that costs the industry £369 billion a year globally: poor product availability. Most people will be very familiar with the experience of products being unavailable in the size/colour they’re looking for, or out-of-stock entirely. In fact, more than most – a survey done in 2019 found that 90% of shoppers had recently at the time (the last 6 months) chosen to leave a store and not make a purchase due to an item being out-of-stock! This problem is caused by low inventory accuracy and subsequently subpar stock replenishment.
If staff don’t have an accurate view of what’s on their shop floors through their IT system, they have no way of consistently ensuring that products are ready to purchase in-store. Many retailers have implemented RFID technology to improve this on floor availability in recent years – driving sales through more accurate inventories and regular replenishment from the backroom.
Product visibility in non-negotiable for retailers embracing omnichannel
We’ve covered it in detail in another article, but after years of flirting with the concept, the pandemic has forced the retail industry to really commit and invest in the omnichannel experience. Services like click-and-collect and ship-from-store have become invaluable in recent times, offering flexibility that works for both customers and retailers alike.
As these services have become more common in the wider industry and more consumers than ever were using services like click-and-collect/curbside last year due to the pandemic, the demand for an omnichannel experience will only increase. Retailers are recognising this and scrambling to adjust, in a recent survey from the Retail Industry Leaders Association (RILA) the number one imperative for the industry was to ‘become omnipotent on omnichannel.’
To make Omnichannel really profitable requires investment. Brands that try and offer services like click-and-collect without the required visibility will find themselves constrained. Either they offer a limited service (relying on safety stock and only selling items they have in surplus) or they offer an unreliable one – routinely cancelling omnichannel orders when they discover items reserved for pickup or delivery are not actually in stock.
Retailers that offer effective and profitable omnichannel services have a real-time digital view of their stock across all channels. To make this work those inventories run on item-level data so that their IT systems can handle items being reserved, shipped-from-store or returned-to-store throughout the day, whilst maintaining a 360’ view of merchandise.
Brands are still working towards gaining visibility over their supply chains
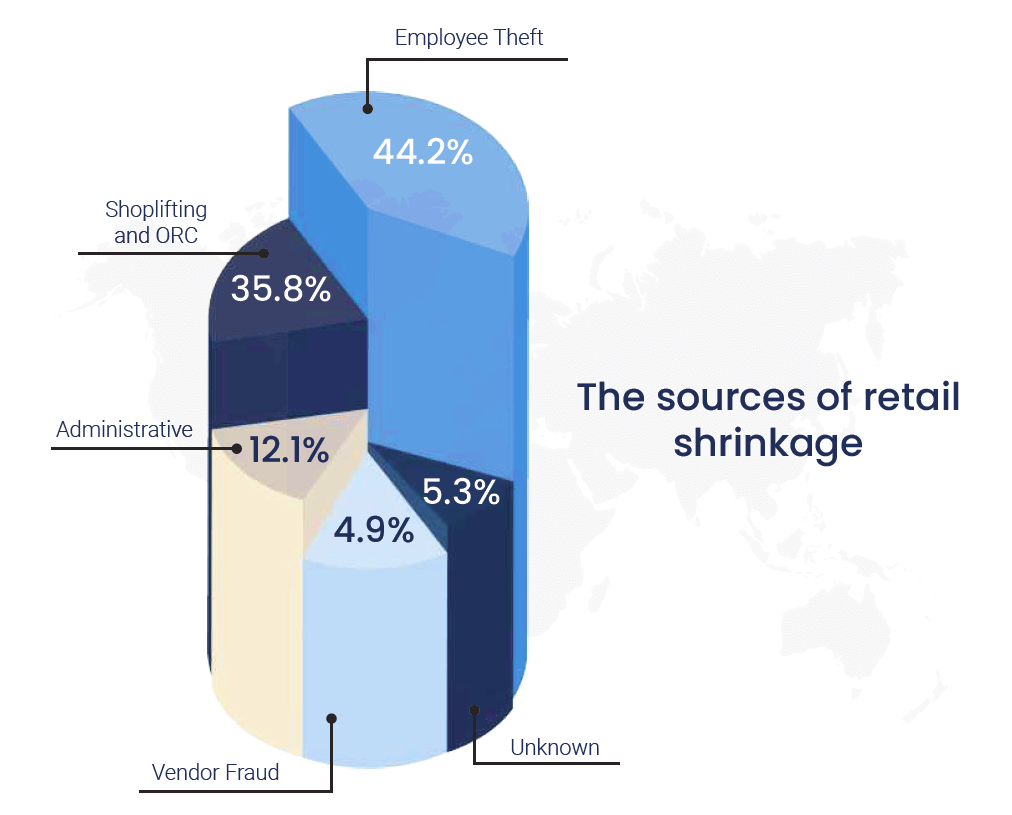
Supply chain visibility is a growing concern for retailers. As supply chains have scaled and become global, issues like inaccuracy, shrinkage and bloated inventories across DCs and stores compound and can become million-dollar issues. For example, UK retailers alone are experiencing annual losses totalling £11 billion due to shrinkage.
Knowing exactly what is passing through each stage of the supply chain is a challenge. With traditional logistic methods working on a carton level and SKU level, retailers struggle to pinpoint where mistakes or shrinkage are occurring. For store networks, this results in stores carrying more products than they need, in the form of both safety stock and ‘phantom stock’ (products that the retailer does not even know about).
This has been something retailers have been aiming towards for some time, in a report by Zebra Technologies in 2017, 72% of retailers said they were working on digitising their supply chains in order to achieve real-time visibility. Fast-forward to 2021 and while progress has been made, there is still work to be done. Brands need to invest in technologies like RFID to be able to track individual products throughout every step of the supply chain.
Not only do these digitised operations reduce the number of shipping mistakes, but the granular data that they work with allows brands to optimise their supply chains to levels simply not possible before such digital transformation.
As new retail models develop – the need for visibility is only going to increase
Retail is going through a period of unprecedented change. We have referenced supply chains and operations growing increasingly complex for retailers in recent years and that is only going to continue in the future. Not only will omnichannel experiences continue to grow and develop, but new models are beginning to emerge that will test brands’ agility and require an item-level view of products.
The key driver for the majority of these new models is sustainability. The push for greener fashion retail experiences, in particular, is still in the early stages but picking up traction rapidly.
Burgeoning new sustainable models like rental, recommerce and the circular economy promise a far eco-friendlier experience than fast fashion. These models will have their challenges however, rather than the one-way traffic of typical retail models, these methods will require a lot of reverse logistics. It’s vital not only that brands can handle this 360’ flow of merchandise, but with rental and second-hand items, in particular, item-level data is vital as products will all be unique.
As visibility becomes a priority, it’s no coincidence RIFD uptake is booming
So, if product visibility is an issue across the retail industry, what are brands doing about it?
Since visibility has become a key issue in the last few years, more and more retailers have begun implementing RFID technology to track and manage products across their businesses, on an item-level, at 99% accuracy and even in real-time.
RFID ticks several boxes that are key to achieving such visibility. First and foremost, it digitises products and processes in DCs and stores, creating a digital record of all items. It also works on an item-level, so is able to distinguish between two products of the same SKU. Finally, RFID processes are efficient enough to be done throughout the supply chain, on a daily basis including inbound and outbound checks as well as daily stocktakes for stores. This means retailers leveraging RFID have a 360’ view of item movement from source-to-store, with granular item-level data that works on a global scale.

Cloud-hosted RFID software
Stock accuracy, on-floor availability, and omnichannel applications in stores.
Detego Store is a cloud-hosted RFID solution which digitises stock management processes, making them more efficient and more accurate. Implemented within hours, our multi-user app can provide intelligent stock takes and a smart in-store replenishment process. Later, you can scale the solution to offer omnichannel services and effectively manage your entire store operations with real-time, item-level inventory visibility and analytics.
It is no exaggeration to say that retail has changed like never before.
For some time, operations have been growing increasingly more complex, and shoppers increasingly more discerning. Now that evolution has been accelerated. Retailers must be flexible in meeting consumer demands in the face of a rapidly changing retail landscape if they hope to succeed.
As the industry recovers, retailers pursuing digital transformation in order to optimize operations, expand omnichannel fulfilment, and enable data-driven decisions are poised to lead the way. One of the foundational technologies providing insight to drive digital transformation? RFID.
It’s been around for a long time, but Radio Frequency Identification technology (RFID to you and me) is picking up momentum in the retail space. Both Forbes and McKinsey & Company have published recent articles on how the technology is becoming key for retailers, with the latter even describing ‘RFID’s renaissance’ within the industry.
While this does show a shift in the sector, a renaissance implies that the technology is making ‘ a comeback of some kind. This is not quite accurate, as the business case for RFID has been steadily growing in retail over the years, but we are approaching a new stage of its lifecycle in the industry. This is a natural cycle for most new and transformative technologies, but the effect of the pandemic on retail has accelerated this. Not only are many brands on thin ice in the aftermath, but one of the key reasons for implementing RFID, delivering an Omnichannel strategy, has evolved from ‘beneficial’ to almost ‘non-negotiable’ since last year.
Let’s explore where RFID has come and more importantly, how it has become one of the single most important operational technologies to retailers in recent years.
RFID and the Technology Curve
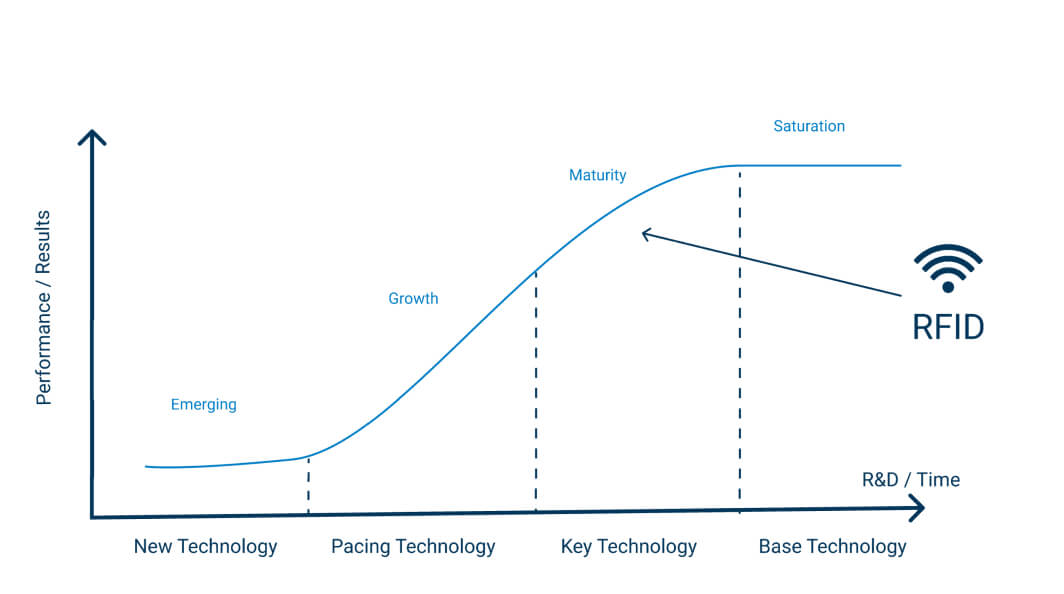
While RFID was invented in the 1940s, it wasn’t until this century it began being used as a business tool. In retail, it has existed for almost 20 years, but its initial cost, technical limitations and fewer established use cases all meant most companies (wisely) didn’t see the value in it initially.
This is common for new technology and over time RFID has matured with more research & development as well as more deployments in live retail environments. This has meant the performance of the technology improved and the return on investment for retailers increased. This is known as a technology S curve (seen below). Over the last ten years, RFID use in retail has experienced this curve with the adoption levels and value for retailers increasing year on year.
Fast-forward to the present day and RFID is at a maturity stage, and we predict that over the next five years will become a ‘base technology’, in apparel and sports retail at the very least. This increase is a result of both the technology maturing over time and the industry evolving as a whole – things like digital disruption, the growth of Omnichannel and the pandemic accelerating certain shifts within the industry have meant the need for RFID has increased greatly.
How has RFID evolved?
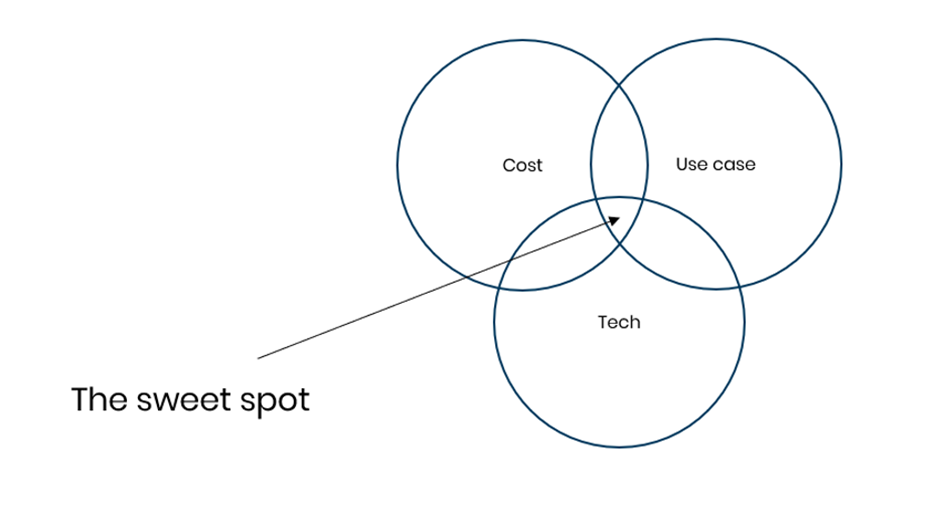
For a technology to take off in business (i.e., for it to have a business case) several factors need to be met. The technology needs to be cost-effective, reliable/easy enough to implement and use and most importantly it needs to have enough valuable applications to make it worth doing in the first place.
Early-stage technologies may have one or two of these down, but to really take off and become saturated within an industry it needs to be in this sweet spot of covering all three. So, how do these requirements stack up for RFID?
Cost
Like any technology, Radio Frequency Identification was expensive when it first came out. Over time as more R&D was done and more providers entered the space, the price has steadily gone down.
The biggest factor in this was the drop in the cost of RFID tags themselves. At the start of the century, a single RFID tag could cost as much as $0.75/£0.50 but in the current market, they can be sourced for as low as $0.04/£0.06. This not only makes for much better margins for any retailer looking at the technology, but it opened up whole new industries or sectors whose lower product prices points originally made RFID unfeasible.
Tech
The technology behind RFID has also developed beyond just price point. RFID hardware has improved in terms of reliability and read distance. Tags on the other hand have become smaller and more advanced so that metal and liquid products no longer interfere with the signal – both of these improvements means a far broader range of merchandise can be tagged. This is particularly relevant for categories like food or cosmetics. Finally, the software has also evolved, with more advanced functionalities like tag localisation, Smart Shielding, and global track-and-trace.
Use case
One of the greatest strengths of RFID has always been its wide range of uses and applications. This can at times be a double-edged sword, as companies may not know where to start, may deploy use cases in a sub-optimal order or may chase all use cases at once.
Thankfully, most RFID providers and experts know that a phased approach prioritising KPIs like stock accuracy is vital to both achieving ROI and laying the foundation for more advanced use cases like enabling omnichannel. Provided the project is scaled in the right way, the uses of the technology are broad and include supply chain visibility and traceability, real-time data applications like automated planograms as well as consumer-facing use cases like smart-fitting rooms.
How Retail is Evolving: Why is RFID Becoming Key?
Most of these major changes in RFID retail technology itself occurred several years – the business case has been solid for the last five years at least. This is why many major retailers like adidas, Levi’s, Nike and Target to name a few already have high levels of RFID integration. But in the industry as a whole this is ramping up but why?
Naturally change often happens on a curve, with more cautious brands hesitant to change until they see positive results from other companies who take the ‘risk’. On top of this, however, the market and consumer is changing fast and the digitised accuracy and visibility that RFID provides are becoming non-negotiables for most retailers.
The need to optimise profits/costs
Any business wants to optimise their costs and maximise their profits – it’s not rocket science. But the best ways to do that can often be unclear, and sometimes if it requires some upfront investment or new technology brands may decide that now is not the time. For retailers, the store model and brick-and-mortar economics have been gradually changing over time. As the balance between online and offline channels continues to shift, some stores may become unprofitable if nothing is done.
That is where so many retailers get upfront value from RFID. Implementing the technology in stores increases sales (from reducing out-of-stocks) and reduces running costs (from smaller inventories & increased operational efficiency). Lean stores optimised to such levels may be a necessity in the future with stores playing a less crucial role than five years ago.
Increasing Omnichannel and digital integration
Omnichannel has been a growing force in retail for the last five years. Many retailers bet on omnichannel early, investing in the technology to digitally integrate their stores and supply chains with their online channels, and have profited as a result.
To succeed in omnichannel investment is required, as services like click-and-collect or store-fulfilment need a real-time digital view of store stock if they are going to work effectively. RFID is the perfect solution to these omnichannel challenges, and it’s no coincidence that as Omnichannel has become more common amongst retailers, RFID has as well.
This will be the single biggest factor for RFIDs growth in the next few years. While Omnichannel was once more of an optional strategy since the pandemic and ever-increasing digital shopping channels – it is becoming non-negotiable. This isn’t just us saying so, retailers themselves have recognised this, in a recent survey from the Retail Industry Leaders Association (RILA) the number one imperative for the industry was to ‘become omnipotent on omnichannel.’
Pandemic accelerating the need for digital transformation
While the need for digital transformation to optimise costs, integrate channels and improve operational visibility has been increasing in recent years, the COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated this. We’ve covered the effects of the Pandemic in detail over the last year, and many of the mid to long-term effects will push more retailers to RFID adoption.
The changes we have just covered, optimising profits and offering an omnichannel experience, were (or should have been) priorities before, but in the aftermath of the pandemic, they will be the difference makers.
Stores, on the whole, are not going anywhere but they will have to adapt to post-pandemic retail – meaning potentially lower in-store sales and a higher proportion of digital and omnichannel activities. The challenge for retailers is trying to adapt to a changing environment while also financially recovering from the peak of pandemic and lockdowns.
For brands that haven’t started their RFID journey the timing is awkward and yet they may not be able to afford to wait too much longer. While Omnichannel services will be the long-term play, smart retailers will look to use RFID to optimise their profits as soon as possible, securing a return of investment and setting themselves up to profit long-term.

Cloud-hosted RFID software
Stock accuracy, on-floor availability, and omnichannel applications in stores.
Detego Store is a cloud-hosted RFID solution which digitises stock management processes, making them more efficient and more accurate. Implemented within hours, our multi-user app can provide intelligent stock takes and a smart in-store replenishment process. Later, you can scale the solution to offer omnichannel services and effectively manage your entire store operations with real-time, item-level inventory visibility and analytics.
Retail has been on a transformation journey ever since the birth of the internet, and the online shopping and digital consumers that came with it.
Many new (often online-first) brands have grown into superpowers, and ‘traditional’ brick-and-mortar retailers have had to adapt their offering in order to stay competitive in what is a dramatically different environment compared to just ten years ago.
Make no mistake, this industry shift as a result of digital channels is still ongoing. While it by no means spells the death of physical retail – the industry must continue to adapt.
Brick-and-mortar retailers selling online, and gradually adopting an omnichannel model, is a big step in this journey.
This gradual shift has been greatly accelerated by the pandemic. While omnichannel was in many retailers five-year plans, the pandemic meant brands had to shift suddenly to survive in a temporary world where online was king.
So, as many retailers are leaning hard into omnichannel – is the industry ready? The operational challenges and costs associated with omnichannel mean some retailers might struggle to really profit. So, what can brands do to change this, and what technology should they invest in to ensure their omnichannel strategy delivers long-term?
The Omnichannel Surge
The pandemic was a big accelerator for the already ongoing digital transformation of retail. The temporary circumstances of the pandemic meant more shoppers were forced online. A report from Nosto claims at the height of lockdowns online channels spiked 66%.
This online spike also affected omnichannel services. Click-and-Collect/BOPIS increased 70 percent by volume and 58 percent by value in 2020, according to ACI Worldwide data. Meanwhile, retailers fulfilling online orders from stores grew by 80% in the US, according to global data.
While spikes like this are temporary, online channels will not return down to pre-pandemic levels. This is not only because of ongoing safety concerns, but because many consumers have been introduced to online channels or omnichannel options like BOPIS & curbside for the first time. Many of these new digital consumers will not give those options up, why would they?
So, while stores are coming back and will remain a key part of retail, the environment that they exist in will have changed, with stores operating as part of online channels rather than in tandem or competition with them.
This isn’t new however – the industry has been talking about the gradual move to omnichannel for a long time. What’s significant is how this sudden spike has forced brands to react and adapt far faster than they would have planned. In fact, the pandemic has accelerated this shift by up to 5 years according to data from IBM.
So, are retailers well-positioned for this sudden spike in omnichannel activity?
Growing Operational Challenges for Omnichannel Stores
For the main two omnichannel activities – BOPIS & Ship-from-store, store staff effectively have to do extra work that the customer or the DC would normally do, respectively. These services have natural advantages for retailers and customers, but without the right support store staff can struggle to fulfil these orders and keep on top of their normal tasks.
When stores are quiet like during the pandemic, this is not an issue and allows you to leverage stores and staff that would otherwise be unproductive. Moving forwards, however, as stores begin to return closer to normal foot-fall levels, staff may be overwhelmed without extra help like more dedicated in-store fulfilment staff or supportive technology.
IT & Inventory Management Improvements Required
Even with the staff and operational manpower to fulfil and deliver these omnichannel services, if a store’s IT system is not up to scratch they will struggle to fulfil orders correctly and deliver on the promises made to customers.
For this to work, brands need a single view of stock across their stores and online shop. For brands to offer reliable and profitable omnichannel services, their inventory management system needs to fulfil three key criteria.
The first is simply accuracy. If stores are running at a standard 70% inventory accuracy, the likelihood of them offering stock to customers that simply isn’t there is too high.
The second – stock needs to be as close to real-time as possible to maintain this accuracy throughout the day. If stock is not updated throughout the day, then it becomes impossible to offer reliable services like BOPIS.
Finally, to do these services effectively it is much more manageable if stock is operating on an item-level rather than an SKU level. This allows stores to easily distinguish between identical items, so ship-from-store or BOPIS can work down to the final remaining SKUs.
Without this infrastructure in place, it’s common for BOPIS or ship-from-store to offer customers stock that isn’t actually there. The result is orders being cancelled shortly after they are made, and customers being disappointed.
Handling Returns
Returns are the Achilles heel of online shopping in general, and omnichannel services are no exception. Not only do returns eat up margins, but they also again require some operational manpower to process and re-distribute, be it at the DC or the store.
This problem is particularly prevalent in apparel and sports retail due to sizes and fit. While apparel stores have a far lower rate of returns than online, when adding BOPIS and ship-from-store and return-to-store into the mix, the rate of returns can increase drastically.
Balancing The Cost of Omnichannel
Managing and making the most of fine profit margins has always been key for successful retailers. When selling across channels in different ways – keeping an eye on the variable profit margins is essential.
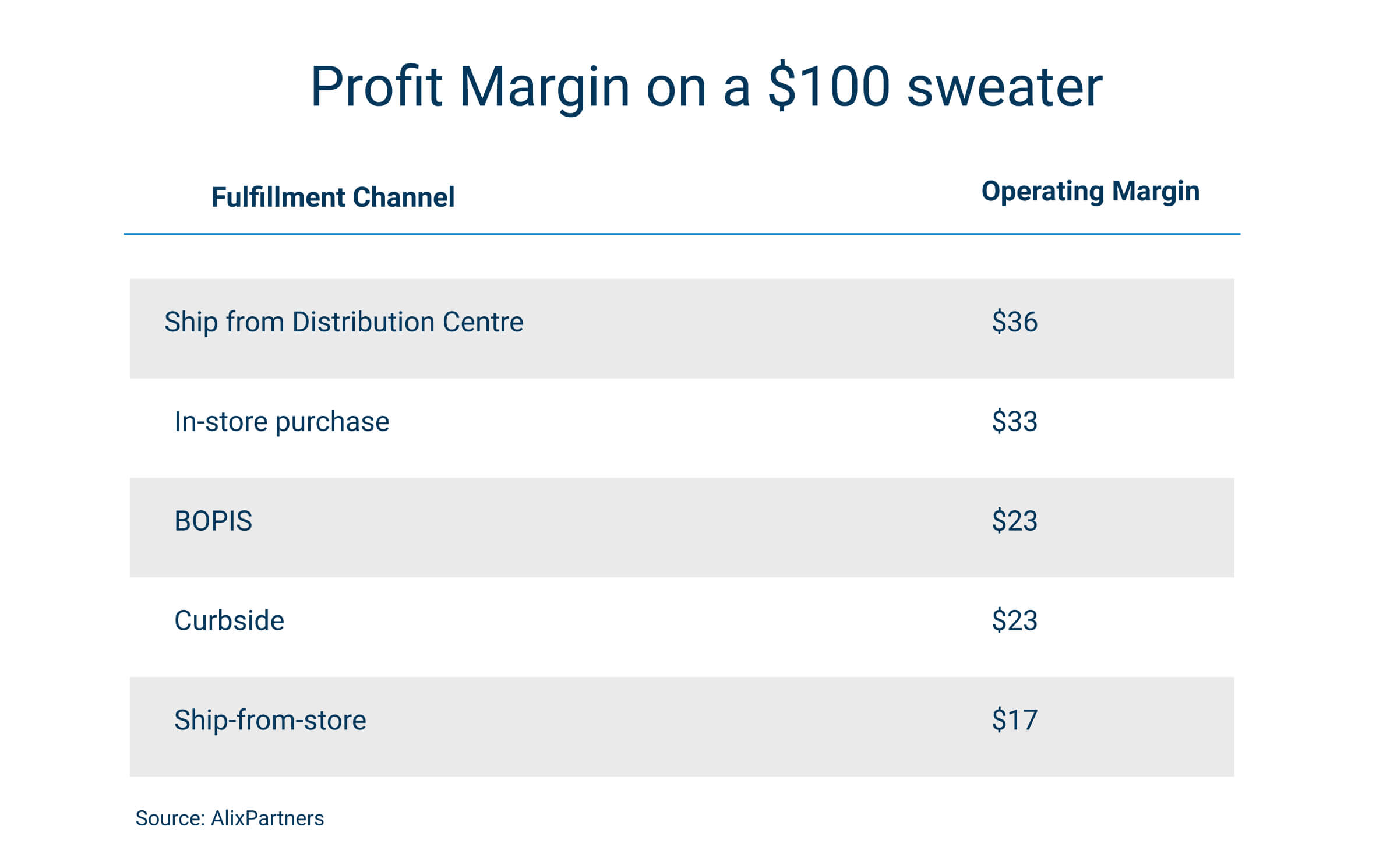
Shipping from DC, also known as direct-to-consumer, is often the most profitable for retailers. This is why we have seen many brands begin to shift to more DTC models. This model has many advantages like bypassing third parties and servicing a larger area than stores, however, factors like returns can quickly have a negative effect on these margins.
Only somewhat less profitable is in-store sales. While rents and staff costs can be considerable, the operational tasks are effectively shared with the customer. While staff operate checkouts and maintain inventory the customer picks and packs their own orders. It may seem strange to think about in-store shopping in those terms, but some customers are beginning to wise up and appreciate the convenience of retailers doing this for them.
As we get to the omnichannel purchase methods, BOPIS (click-and-collect) and curbside, the operating margin is somewhat worse due to the fact that store staff have to pick and fulfil orders from the shopfloor or backroom. For curbside, there is also the added strain of carrying orders out of the shop to give to customers.
Finally, the most severe operating margin belongs to ship-from-store. This is because you have store running costs on top of in-store fulfilment as well as delivery costs. Despite this, we are seeing many major retailers lean into ship-from-store as a way to boost store sales and leverage store inventories. For example, Target fulfilled 75% of their digital sales using ship-from-store in Q2 last year.
Essentially, these models are all worth doing as they bring in additional customers and sales. Customer expectations are growing, and shoppers want to purchase and revive their products in whatever way suits them best, if you don’t meet those expectations, your competitor will.
However, for more operationally intensive models like ship-from-store and curbside pickup, it’s important to make sure these services are run as efficiently as possible, particularly when done at scale.
So, how can brands meet these challenges and ensure their omnichannel operating margins are as healthy as possible?
How RFID Delivers the Perfect Foundations for Omnichannel Services
Like we said earlier, the concept of Omnichannel retailing has been around for a while. Even before the pandemic, many forward-thinking retailers were beginning to invest in and build out their omnichannel capabilities.
To meet the operational challenge this meant setting up the new processes that go alongside BOPIS or ship-from-store and ideally adding more staff to support these processes. The IT challenges, particularly in terms of inventory and order management, require some more investment and technology integration.
When it comes to delivering the IT requirements for this, Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is the single solution. While the deliverables of stock accuracy and product availability can provide a ROI for stores by themselves, laying the foundation for strong omnichannel services is often touted as the main reason for retailers choosing to implement the technology.
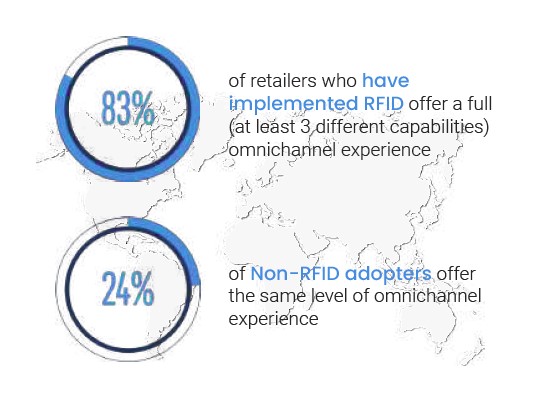
In a 2018 study, 83% of RFID adopters offered three or more omnichannel fulfilment options compared to only 24% of non-adopters. This is because RFID delivers a highly accurate and even-real time view of inventory at scale and across channels.
This single view of stock means retailers (and their customers) know exactly what is in stock at all times, making it easy to sell store stock online. Because RFID inventories work on an item level, these services can be completely granular, reserving individual items without even disappointing customers by offering them products that aren’t really there.

Cloud-hosted RFID software
Stock accuracy, on-floor availability, and omnichannel applications in stores.
Detego Store is a cloud-hosted RFID solution which digitises stock management processes, making them more efficient and more accurate. Implemented within hours, our multi-user app can provide intelligent stock takes and a smart in-store replenishment process. Later, you can scale the solution to offer omnichannel services and effectively manage your entire store operations with real-time, item-level inventory visibility and analytics.
Beauty retail is an industry at a crossroads. A sector resilient to crisis and change compared to other retail categories, cosmetic brands are beginning to feel the effects of the pandemic and ongoing industry changes.
In recent years, apparel and sports retailers have undergone digital transformations to stay competitive, and now beauty brands have an opportunity to follow suit. Read this eBook to discover how and why beauty retailing is set to transform into the industry of the future.
Beauty retail: An industry at a Crossroads
The apparel and sports retail industry have undergone mass change over recent years. Such retailers have undertaken digital transformation journeys in their store and distribution networks to adapt to digital-first customers and eCommerce competition. The beauty sector, however, is still behind the curve.
In most major beauty-industry markets, in-store shopping accounted for up to 85 per cent of beauty product purchases before the COVID-19 crisis – (McKinsey&Co) making the level of eCommerce penetration lower than in other retail sectors. While retailers in other categories have been forced to innovate and adapt in the face of falling brick-and-mortar sales, competition from eCommerce and direct-to-consumer models, brick-and-mortar beauty sales were more resilient.
But this is changing. Not only are eCommerce levels steadily increasing year-on-year, but the COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated this drastically, driving five years of change in a single year, according to
IBM. This leaves brick-and-mortar beauty retailers on unsteady ground. Beyond this, brands will have to navigate a more digital-centric environment and optimise margins to cope with reduced sales.
The good news is many of the challenges that are now facing beauty have been facing apparel or CPG for years. The digital solutions and strategies that have allowed apparel to adapt are well established and ready to deploy to the sector. The digital transformations that many apparel and sports retailers were forced to undergo will not only fit beauty retailers but will also help them solve older challenges. Beauty retailers may need to go on a similar journey to apparel, but the tracks are there to follow.
What is in the eBook?
- Beauty retailing at a crossroads
- Bringing beauty operations up-to-speed
- Accuracy redefining margins
- Fixing beauty’s shrinkage problem
- Catching up with the omnichannel trend
- Countering the Gray Market
- Becoming digital and analytics leaders

As we look to round off what has been an incredibly disrupting year with the all-important holiday season, how is the retail industry likely to fair? Will the usually busy holiday season provide some much-needed relief to retailers feeling the pinch of a tough year, or will sales and profits continue to struggle? We analyse the figures and identify the key trends that will rule this year’s holiday season.
Overview
In terms of general outlook, the majority of experts are predicting the coming season to be positive in general, but with less growth compared to previous years. ICSC and CBRE both predict less than 2% growth in sales for the period, compared to the average of 4.1% we typically see in the holiday season. Considering the economic and social disruption of the past year this lower than normal increase is to be expected, but ultimately will cap off what has been several months of steady growth in both the UK and the US. If we look at consumer polls, the outlook is similar, with a survey from Maybe* finding that its ‘Christmas as usual’ for 71% meaning they plan on spending the same as in ‘normal’ years. But the way customers, and indeed retailers, go about this holiday season looks to be very different from previous years.
Let’s take a look at some of the key trends for the upcoming holiday season:
An extended season
Black Friday is the event that kicks off the holiday season, typically meaning high discounts, crammed shop floors and long ques outside of stores. Due to the realities of the pandemic many retailers have extended their Black Friday offerings to cover several days or even weeks, in an attempt to prevent overcrowding in stores. COVID may have moved the starting line of the season altogether however with prime day, typically taking place in July, pushed back to earlier in October. If ever there was a retailer big enough to move the needle by themselves, it was Amazon – and several retailers in the US including Target and Walmart launched their own deals at the same time to compete with the online giant. Customers will be keen to take advantage of these deals this year more than ever, and according to AlixPartners, 49% of consumers plan to start their holiday shopping by Halloween or earlier in the US, and in the UK Maybe*’s survey found that 65% of respondents have already started their Christmas shopping this year.
ECommerce will continue to run the show
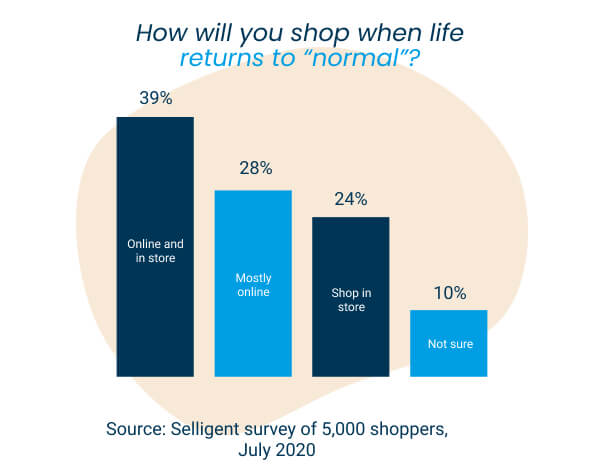
It’s a statement everyone in the industry is very familiar with this year, but the defining feature of this holiday season will be a major preference for online shopping and eCommerce. While this trend has been steadily increasing over the years, the coronavirus pandemic has caused a huge spike in eCommerce as many consumers avoid stores and practise social distancing. As a result, Deloitte’s Annual Holiday Retail Forecast predicts eCommerce sales will grow between 25-35% year-on-year, compared to 14.7% in 2019. Similarly, the Maybe* consumer survey found a whopping 58% of customers plan to do their Christmas shopping online this year. This will be a test for many retailers, both pure-play and multichannel models, as the increased demand will test the capacity and strength of both their online channels and their fulfilment capabilities.
How will Brick and Mortar stores fare?
But what of the brick-and-mortar store? It’s no secret that physical retail has taken the brunt of the impact on sales and revenue this year, but will the holiday season offer some respite? Retailers hoping to make the most of the period will need to focus on ensuring safety and customer confidence in their stores, with 55% of consumers saying that COVID-19 safety tops their list of holiday shopping concerns according to a survey by PwC. Even with these measures in place, in-store holiday traffic is expected to drop by up to 25% this year in the US. For the UK, it may be even worse, with only 30% of shoppers heading to their local high street for Christmas, according to Maybe*. Black Friday specifically is where store traffic is likely to fall more than ever, with more than a third of US shoppers planning to avoid stores for Black Friday in the US, and a massive 91% said the same for the UK.
Bigger discounts for Black Friday?
So how are retailers planning to approach this year’s Black Friday to account for this? Alongside the extension of the event and the repositioning online, it seems many retailers are planning on discounting deeper and earlier this year. According to data analytics experts Edited, the most common advertised discount this year is 40-50% for apparel products compared to an average of 20-30% the previous year. For fashion retailers, in particular, this makes sense as the goal is to not only try and drive sales but is, perhaps, more importantly, an opportunity to sell older and slow-moving seasonal stock collected throughout this challenging year.
Store fulfilment will be vital for many
With the continued dominance of eCommerce, non-pure-play retailers are being challenged to keep up with the pace as their online channels have been, at least temporarily, promoted from supporting operations to the heart of the business. Two of the biggest retailers in the US have invested heavily in their ship-from-store capabilities this year, with Walmart expanded theirs to 2,500 locations, whilst target reported fulfilling 90% of their online orders from store cutting the cost of fulfilment by 30%. Adopting such a strategy not only allows for such operational benefits but it makes the existing eCommerce arm much more durable – which is exactly what they’ll need to be this season.
Click-and-collect / Curbside continue to be popular purchase options
Similarly, click-and-collect and Curbside services will be more important than ever for many retailers this season. Macy’s CEO called the use of Curbside a ‘big secret weapon’ for the upcoming holiday season. Just how secret it is may be up for some debate, according to customer surveys, 80% of shoppers expect to increase their use of these services over the next six months, and 85% have already significantly increased their use of curbside since the year began. The reason for this is clear as such services tick all the boxes of being convenient, safe and online-first.
‘The season will ultimately cap off what has been several months of steady growth in both the UK and the US.’
‘COVID may have moved the starting line of the season altogether however…’
‘eCommerce sales (are predicted to) grow between 25-35% year-on-year, compared to 14.7% in 2019.’
‘Retailers hoping to make the most of the period will need to focus on ensuring safety and customer confidence in their stores’
‘it seems many retailers are planning on discounting deeper and earlier this year’
‘online channels have been, at least temporarily, promoted from supporting operations to the heart of the business.’
‘80% of shoppers expect to increase their use of these services over the next six months’
Want the latest retail and retail tech insights directly to your inbox?
Omnichannel retailing, offering customers a unified and convenient experience across and between shopping channels, has exploded back into relevance this year. For those in the industry, it might feel like it’s been around for ages – and it has. So long in fact that omnichannel grew into a buzzword that was thrown around relentlessly to the point that the term was declared ‘dead’ by many. The reports of Omnichannel’s death have been greatly exaggerated, however, with the ability to serve customers across multiple channels becoming a life raft for many retailers this year. While the conditions faced this year will be once-in-a-lifetime, many of the effects and trends may be long-term.
What exactly is Omnichannel retailing?
In short, omnichannel is the perfect connection and interplay between a brand’s physical and digital channels. A pie in the sky omnichannel experience is one where the differences or barriers between shopping in-store, online or on a brands app do not exist. You can check a physical stores stock levels on an app, the webshop remembers what you purchased in-store and uses it to recommend you more relevant products and so on. More grounded and familiar examples of this type of retailing are services like click-and-collect (Buy-online-pick-up-in-store) or ship-from-store (buy-online-ship-from-store).
Omnichannel was born from the need for (traditionally) brick-and-mortar brands to compete with online shopping. When retailers tried (and failed) to compete with established eCommerce giants such as Amazon or ASOS by simply launching webshops of their own (Multichannel retailing), they took it one step further. Rather than beat the likes of Amazon at their own game, retailers began doing something Amazon (at the time at least) couldn’t do – leveraging both their physical and digital channels, not in tandem but in unison. For this to work the connection between these channels should be as seamless as possible, so that it stops being the brand’s online experience bleeding into the physical, or vice versa, and it simply becomes the single brand experience.
This move towards omnichannel can come from both directions, as in recent years we have seen pure-play eCommerce brands expand into stores. Amazon for example is building futuristic stores which use customers’ existing amazon accounts instead of checkouts, and are filled with advanced retail technology, blurring the line between physical and digital. Not only is this a unique example of an omnichannel offering but it shows the fact that an omnichannel approach is not just for brick-and-mortar retailers trying to stay competitive, even the ‘disruptor’ e-tailers are repositioning to an omnichannel offering.
2020 and the Omnichannel revival
The effect of COVID-19 on retail has been well reported so we won’t delve into that here. The key conditions for the relevance of omnichannel are the huge spike in eCommerce and customers reluctance to return to stores. A report from Nosto claims at the height of lockdowns online channels spiked 66%, and a separate report from Klarna found that 71% of shoppers are putting off doing their Christmas shopping in-store this year due to COVID concerns. Whilst brick-and-mortar sales struggling or stopping entirely was bad news for any retailer, brands that have more advanced digital and omnichannel capabilities have weathered the storm far better. They have done this by being flexible and serving the customer wherever is more convenient and comfortable for them. Whilst for many this is online for others it is a mixture of both. This is where the interplay between channels with services like curbside can make a real impact.
The demand for click-and-collect & curbside is higher than ever
As stores have re-opened, many customers want to purchase products from their local stores but are still cautious about fully returning to in-store shopping. Buy-online-pick-up-from-store (BOPIS) offers a convenient and safe solution to these concerns. Customers can check online what stock their local store has available; purchase items online and then collect from the store the same day. This offers a convenient and contact-free alternative to shopping in-store, with Curbside pickup the same concept except customer don’t even have to enter the store. According to customer surveys, 80% of shoppers expect to increase their use of these services over the next six months, and 85% have already significantly increased their use of curbside since the year began. Whilst the initial spike in demand for these services was due to COVID-19, as customers grow accustomed to the convenience, the demand for BOPIS will continue well beyond the pandemic.
Ship-from-store is proving decisive in the online-centric New Normal
On the other side of the omnichannel coin, we’ve seen many retailers absorb the eCommerce bump through the use of ship-from-store. Simply put, ship-from-store involves fulfilling online orders using store stock, effectively leveraging stores as miniature distribution centres. The benefits of this under normal circumstances are already significant, such as cutting down on last-mile fulfilment and offering customers more stock. During the pandemic, however, ship-from-store was a lifesaver for many, allowing brands to not only capitalise on increased online orders but to leverage quiet or even closed stores to prevent unsold inventory piling up. Two of the largest retailers in the USA have been betting heavily on ship-from-store this year, not only as a way to ride the wave of the pandemic but to even compete with the power of Amazon. Walmart expanded their ship-from-store capabilities to 2,500 locations earlier in the year, whilst target reported fulfilling 90% of their online orders from store cutting the cost of fulfilment by 30% and overseeing 100% increase in digital sales YoY.
A temporary blip, or a permanent shift?
The key question is of course, how temporary is this change? As things start to get better around the world, will brands who have bent over backwards to reposition to the ‘new normal’ only find themselves at a loss if things completely revert back to normal? While the drastic increases to eCommerce will fall off a certain extent, in the long-term it will remain higher than pre-pandemic levels. The report from Nosto suggests that this is now levelling off to an average increase of 7%. Not only does this mean the business case for omnichannel services is still stronger than it was at the start of the year, but as customers have relied on services like online and curbside out of necessity, in the future they will continue to demand it of a preference for convenience.
What do retailers need in order to offer a strong omnichannel experience?
So, what are the requirements for retailers attempting to offer their customers these services and experience? Whilst it does depend on how advanced the offering is, the fundamentals are digitisation and integration across all channels.
Expert Chris Walton says there are three foundations to omnichannel retailing:
- Cloud commerce
- Real-time Data Capture and Applications
- Location and Context Analytics
For services like click-and-collect and ship-from-store, the first two points are key. The cloud is needed for the sharing of information, both between the retailers two channels (the store and webshop) and between the retailer and the customer. The data capture is vital for these services to be accurate as to sell products in-store to online customers, retailers need to know exactly what is in stock in their stores to an individual item level. This is why RFID is a key component of omnichannel retailing as it offers the real-time visibility of the products and the high 99% stock accuracy so retailers can offer omnichannel services with confidence.
Want to find out what it takes to implement RFID in retail? Register for our upcoming webinar:
Discover how retail RFID is changing the industry for good. This eBook will guide you through the top 10 needs identified by retailers to ensure sustainable success in the modern environment. Explore the common challenges preventing retailers from achieving their goals and learn how applying smart RFID-based solutions delivers consistently good results.
What is in the eBook?
The retail industry is currently ruled by change. The digital age has seen a huge growth in competition from e-commerce and a rapid shift in consumer preferences. This shift has altered the industry greatly with modern ‘omnichannel’ customers demanding to shop where they want, how they want and when they want. Delivering such an experience is a challenge, one that requires brick-and-mortar retailers to change.
In this eBook, we analyse the top 10 needs identified by retailers to ensure sustainable success in the modern environment. Within each of these needs, we identify the challenges often preventing retailers from achieving them, and how applying smart RFID-based solutions can deliver consistently good results.
Improving key metrics in stores
- How retailers use RFID for quick and efficient stocktakes and cycle counts
- Improving stock accuracy in stores
- How smart solutions are being put to use for item-level replenishment, ensuring products and sizes are always available to be sold.
Delivering to customers with retail RFID
- How stores can reduce common customer friction points
- The relationship between RFID and effective omnichannel services
- The advanced retail RFID solutions that improve the in-store customer experience like chatbots and smart fitting rooms.
Optimising supply chains from source to store with automated processes
- How to achieve supply chain visibility with real-time info on the movement of products inside and across individual stores and distribution stages.
- How RFID is used to aid logistics at distribution centres, including automated processes like exception handling and order picking.
- What RFID means for retailers’ data and analytics capabilities, such as advanced supply chain traceability and new KPIs for stores and DC’s.

Protecting brands and products from theft, counterfeits and the grey market.
- How RFID can be used to monitor and reduce shrinkage, including theft, both in stores and across the entire supply chain.
- How brands are combatting counterfeit goods by tagging and tracing their products with RFID.
- What the Grey Market means for retail and how several major brands use RFID traceability to locate and stop the source of grey market products.